Safe Practices for Working at Heights
Table of Contents
- Planning and Risk Assessment
- Proper Training and Supervision
- Use of Appropriate Fall Protection Equipment
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance of Equipment
- Maintaining Three Points of Contact
- Establishing Clear Communication
- Adhering to Legal and Regulatory Requirements
- Conclusion
Every year, countless workers face the risk of falls and serious injuries due to inadequate safety measures when working at heights. Whether on construction sites, industrial facilities, or even small maintenance jobs, prioritizing safety is both a regulatory requirement and a moral imperative. By adhering to established protocols and leveraging proper fall protection equipment available from trusted suppliers like Diverse Supply Inc, organizations can take significant strides in keeping their teams safe while performing tasks elevated above ground level.
Effective safety practices at heights involve more than just equipment; they require comprehensive planning, ongoing training, and a culture that values every worker’s well-being. With proper forethought and routine procedures, risks can be systematically reduced, ensuring a safer work environment without compromising productivity.
Planning and Risk Assessment
Before any job begins, a thorough planning and risk assessment phase is essential. This process involves systematically identifying potential hazards associated with work at height, such as unstable surfaces, inclement weather, and electrical hazards. Consider all possible outcomes and plan accordingly to either eliminate the risk, minimize exposure, or put safeguards in place.
Assessments should also factor in the specific environment, tools to be used, and the physical condition of each worker slated for the task. Consult with team members and safety professionals to ensure no detail is overlooked. By deploying structured planning, teams can anticipate and avoid many accidents before they occur. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) offers comprehensive guidelines to help employers create effective safety plans for elevated workspaces.
Proper Training and Supervision
Training is a cornerstone of height safety. Workers must receive both initial and refresher training on using fall protection equipment, recognizing hazards, and following emergency procedures. Training should also be tailored to different skill levels and roles; new hires, for instance, may require closer supervision and more frequent instruction compared to experienced team members.
Continuous supervision fosters a culture of accountability and caution, particularly during comp-risk jobs. Supervisors should be well-versed in the latest safety standards and approachable for questions or concerns. According to the National Safety Council, well-trained and supervised employees are far less likely to be involved in workplace accidents.
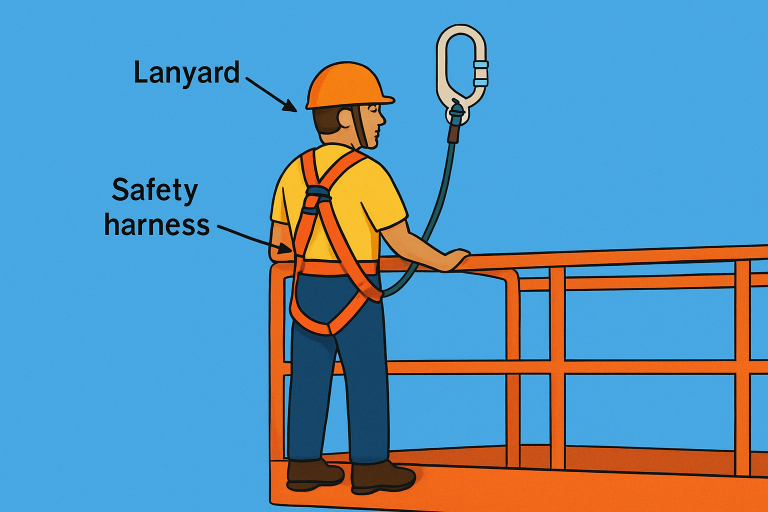
Use of Appropriate Fall Protection Equipment
Using the correct fall protection equipment is vital for minimizing risks. Harnesses, anchor points, lanyards, guardrails, and safety nets offer varying degrees of protection and should be selected based on the unique demands of each task. Ensuring that all equipment meets established standards and is compatible with the specific work environment further enhances safety.
The right equipment not only prevents most falls but can drastically reduce injury severity if an incident does occur. Always verify that gear is properly fitted to each individual worker and that they understand inspection and donning procedures.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance of Equipment
Equipment reliability depends on regular inspection and maintenance. Before every use, employees should conduct visual and tactile checks for wear, fraying, or damage. More thorough periodic inspections should be scheduled and performed by qualified personnel familiar with the specific brand and style of the equipment in use.
Maintenance routines should include cleaning, proper storage, and timely repairs. Defective or outdated equipment should be tagged and removed from service immediately. Proactive inspections and maintenance routines drastically minimize equipment failure rates and improve confidence among workers using this life-saving gear.
Maintaining Three Points of Contact
Stability is crucial for workers scaling ladders, scaffolding, or other vertical structures. Maintaining three points of contact, whether with hands or feet, provides extra stability and reduces the risk of slips, trips, or sudden falls. This practice is simple and easily understood, yet frequently neglected at the moment when focus should be sharpest.
Workers should be reminded regularly of this fundamental safety rule, and supervisors should ensure compliance on all relevant tasks. Visual reminders in the workplace and periodic coaching can make adherence second nature among the teams.
Establishing Clear Communication
Clear, uninterrupted communication can mean the difference between a close call and a catastrophic fall. Utilize radios, mobile devices, pre-agreed hand signals, or other methods depending on the noise level and nature of the job site. Communication protocols should be established before the job and reinforced throughout the project’s duration.
Timely alerts about hazards, shifting plans, or emergencies must be conveyed clearly and quickly to everyone working at height. Encourage a culture where workers do not hesitate to share observations or voice concerns, as this transparency will save lives over time.
Adhering to Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Compliance with all local, state, and federal regulations is non-negotiable and forms the foundation for all other safety practices. Standards set forth by agencies such as OSHA specify both best practices and required procedures for a wide range of industries and job functions. Organizations must remain vigilant to updates and changes in these regulations and ensure full compliance at all times.
Providing ongoing education and access to resources, such as the OSHA website, helps ensure that employers and employees are both aware of their responsibilities and rights regarding safety at heights.
Conclusion
Maintaining a safe environment for those working at heights is a continuous commitment. By embracing thoughtful planning, diligent training, appropriate equipment, and regular communication, employers lay the groundwork for fewer accidents and greater peace of mind on every project. Every worker deserves to return home safely each day, and adherence to these practices is key to achieving that goal.





