Innovative Safety Practices for Working at Heights
Key Takeaways
- Modern harnesses increase both comfort and user safety with advanced features.
- Self-retracting lifelines dramatically improve fall arrest capabilities.
- Virtual reality-based training equips workers for real-world scenarios without exposing them to real-world risks.
- Wearable smart technology delivers actionable, real-time safety data on-site.
- Drones enable safe and precise inspections in hazardous, high-altitude environments.
Working at heights remains one of the most hazardous activities across various industries, including construction, utilities, and maintenance. Advancements in safety equipment and technology have made it easier than ever to safeguard workers on the job. With organizations like platforms and ladders supporting workspace safety and practical access solutions, staying ahead with best practices is now more accessible. These new developments are helping organizations lower incident rates and promote a culture of safety from the ground up.
Employers are responsible not only for meeting current standards but also for seeking out innovative approaches that offer superior protection and training. The rapid pace of change in height safety technology necessitates ongoing education and adoption. By integrating advanced harness systems, digital monitoring, and alternative inspection methods, companies can make significant strides towards a safer work environment. Many industry leaders understand that reducing risk at height is not just about compliance—it’s about utilizing every available means to protect valued employees.
Advanced Harness Technology
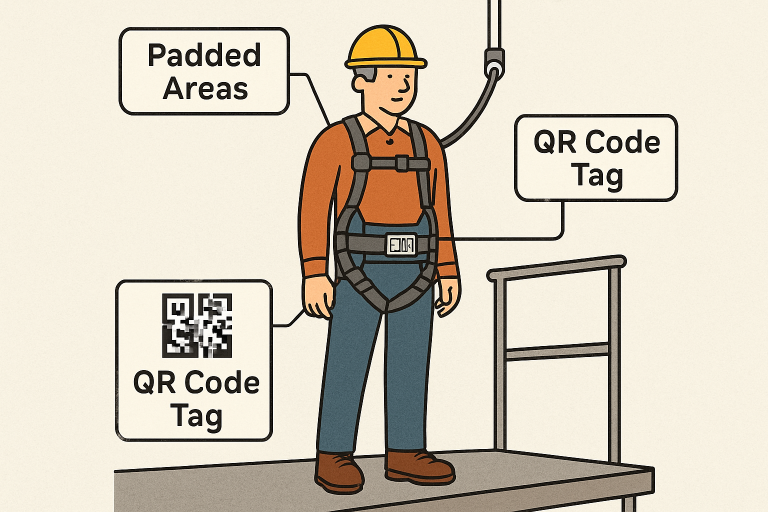
Protective harnesses are a cornerstone of height safety. Next-generation designs focus on preventing common complaints such as fatigue, restricted mobility, and discomfort. Newer harnesses utilize breathable, lightweight fabrics and ergonomic padding that relieves pressure from the shoulders, neck, and thighs. Many also feature clearly visible impact indicators—vital for ensuring harnesses subjected to a fall are tagged out and replaced without delay.
In addition to comfort, technology integration is on the rise, with RFID tags for tracking inspections and quick-release buckles for faster donning and doffing. A growing number of harnesses can interface with digital platforms to maintain certification records and alert safety officers about their maintenance and usage histories. These systems enable organizations to ensure compliance while maximizing both usability and protection.
Self-Retracting Lifelines
Self-retracting lifelines represent an evolution of traditional lanyards, providing more dynamic fall protection. Unlike static systems, SRLs automatically extend and retract as the worker moves, which minimizes slack and the risk of entanglement or tripping. A key safety improvement is the “lock-on-fall” mechanism: should a fall occur, the device immediately arrests it, reducing both free-fall distance and shock load transferred to the user’s body.
Modern SRLs are engineered with lighter, durable materials and sophisticated energy-absorbing technology. Some models even incorporate IoT sensors that provide supervisors with instant alerts if a fall is detected, ensuring assistance is dispatched in seconds. These advances make SRLs a vital part of any modern fall protection system, especially in construction and industrial maintenance.
Virtual Reality Training
Training workers to recognize and react to hazards at height saves lives. Virtual reality (VR) technology offers realistic, immersive environments where employees can safely practice procedures and make critical decisions. By simulating various scenarios—such as windy conditions, equipment failure, or rescue drills—VR allows trainees to experience consequences without the risk.
Such hands-on simulations have been proven to boost knowledge retention and hazard awareness more effectively than classroom instruction. Companies are increasingly adopting VR as a cost-effective, repeatable, and scalable way to deliver high-quality safety education.
Wearable Technology
Wearable safety devices—ranging from smart harnesses to body-worn sensors—are transforming real-time protection for workers at heights. These devices continuously track motion, GPS location, and monitor for dangerous physiological changes, such as fatigue or heat stress. When a risk threshold is breached, instant alerts are sent to supervisors or even trigger automatic safety mechanisms, such as deploying airbags in the event of a fall.
Wearable tech not only bolsters emergency response but also provides valuable data for improving worksite safety protocols over time. Predictive analytics, powered by aggregated device data, can highlight patterns and prevent injuries before they occur. Incorporating wearable technology is one of the fastest-growing trends in occupational safety management worldwide.
Drones in Safety Inspections
Drones are revolutionizing inspection, maintenance, and survey tasks at heights that were previously considered dangerous. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and specialized sensors, drones enable inspectors to remotely inspect rooftops, antenna towers, bridges, and even wind turbines. This reduces the need for workers to climb ladders, scaffolds, or other precarious positions, thereby drastically lowering exposure to fall hazards.
The use of drones is not only safer but also improves efficiency and precision in high-risk asset management. Regular drone inspections can uncover structural issues or maintenance needs that might otherwise be missed, enabling preemptive action. As regulatory guidelines evolve, drone applications are expected to become a standard tool for safety-first industries.
Conclusion
Innovation is transforming workplace safety for those who work at heights. Adopting state-of-the-art harnesses, lifelines, VR simulations, wearable sensors, and drone support enables organizations to set new benchmarks in protection. By investing in these advanced safety practices as a priority, industries can not only meet regulatory requirements but also foster a proactive safety culture that keeps every worker out of harm’s way.



