What Are Infertility In Women And Its Remedy?
Female infertility
The medical definition of feminine Infertility is when a woman is not able to conceive a child after 12 weeks of normal intercourse with her spouse without using contraception.
Infertility in women is characterized from the inability to get pregnant after frequently having unprotected intercourse for a minimum of one year. Following a woman reaches age 35, she’s deemed infertile when she and her spouse are not able to become pregnant after six weeks of trying.
The Odds of becoming pregnant decrease significantly later a woman reaches age 40.
For Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), 1 in 7 partners (about 14%) experience infertility. In such scenarios, one third of infertility cases are brought on by female factors. Nearly as many instances are because of factors involving both spouses, and male factor infertility accounts for approximately 20 percent of instances. Male infertility factors make it essential for both spouses to have fertility testing before a woman starting fertility therapy.
Symptoms of infertility in women
Many women experiencing infertility reveal no. Symptoms, aside from the inability to conceive. If a girl does reveal infertility symptoms, they might include:
- Irregular menstrual cycle or no menstrual cycle.
- Fat Loss
Other Many Reasons are possible for Female infertility. You should contact a Fertility Specialist for this and Planet Women is the Best Fertility Hospital Ahmedabad.
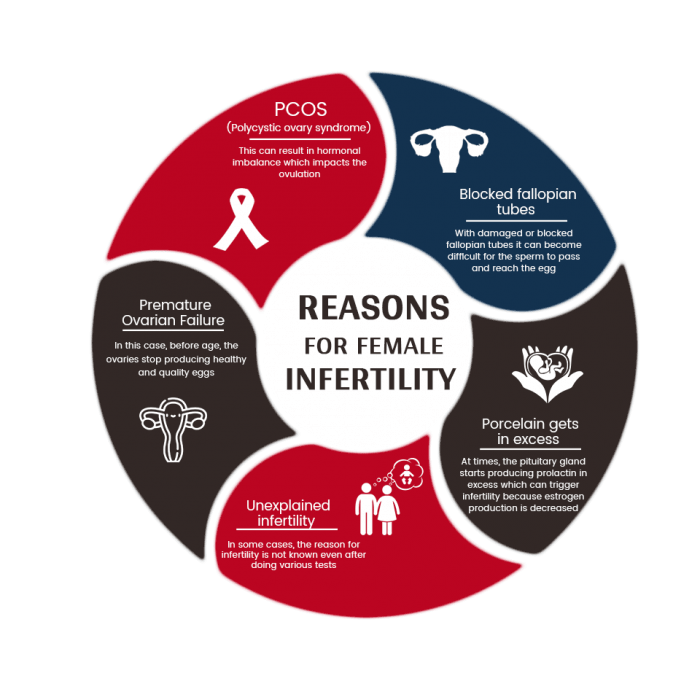
Many factors can lead to infertility in women, Such as:
- Anovulation is the reason for approximately 25% of female infertility and happens when a female’s ovaries aren’t producing or releasing an egg in a standard speed during puberty.
- Female aging induces the amount and quality of eggs to reduce.
- Diminished ovarian reserve takes place when a woman doesn’t have sufficient prospective eggs left in the uterus, or so the eggs are reduced quality, lessening opportunities to conceive.
- Fibroids or polyps are noncancerous tumors that develop from the uterus and may change the form of the uterus or influence the capability of the endometrium to get an embryo (fertilized egg) correctly for implantation.
- Hormone imbalance takes place when a female’s reproductive system generates less than more than the number of hormones required to become pregnant.
- Menopause takes place when a woman stops to have menstrual periods (if the ovaries no longer have viable eggs). In accordance with ASRM, almost 10% of women of childbearing age in the U.S. have PCOS.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a disease in the female reproductive system, generally leading to sexually transmitted diseases or diseases. PID may result in the fallopian tubes, ovaries and/or uterus getting damaged or disoriented. A small fraction of polyps can lead to cancer but many are benign. Uterine polyps can lead to infertility by harmful the uterine lining, inhibiting an embryo’s ability to augmentation for pregnancy.
- Recurrent miscarriage is when a girl experiences at two pregnancy losses consecutively because of an infertility illness or hereditary disorder.
- Unexplained infertility is decided after the two male and female partners are examined for infertility however no recognized cause is set. Unexplained infertility affects almost 10 percent of couples undergoing infertility.
ASRM accounts that 85% of female infertility cases under Medical care are treated with fertility medications or surgery. The suggested course of treatment may vary for each woman according to her unique conditions, including age, length of infertility and total wellbeing.
Also Read Reasons For Failed Fertility Treatments
Some remedies for infertility in women include:
- Lifestyle changes might help alleviate and manage chronic health conditions which could lead to infertility, such as smoking or obesity.
- Ovulation induction utilizes hormone medications that will help signal the ovaries to develop and release eggs which have attained maturation.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a kind of artificial insemination where a fertility specialist can fit semen from a spouse or donor to the female’s uterus. It’s frequently done to fight male infertility conditions which make it hard for sperm to get to the female’s egg.
- Minimally invasive operation can remove or fix a female’s damaged tissue or organs which cause her reproductive system to not work correctly.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is a laboratory process utilized throughout some IVF cycles where healthy sperm (gathered in the male spouse ) is put into the cytoplasm of a female’s egg (collected during the initial portion of IVF) to get a better chance of childbirth and growth of a healthy embryo.
- Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) decides if a particular genetic condition exists within an embryo(s) before implantation through IVF.
- Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) is an evaluation that assesses an embryo(s) for many chromosomal abnormalities and may also be employed to ascertain the gender of an embryo (to prevent gender-specific genetic conditions from the infant).
- Assisted hatching is a remedy during IVF in which the outer coating of an embryo is punctured to help in its attachment (called hatching) from the uterus, increasing the probability of implantation and pregnancy.
- Donor eggs or donor embryos could possibly be utilized in women that cannot conceive using their own eggs or embryos.
- Gestational carriers or surrogates are girls who carry a pregnancy to term for a female who might not have the capability to take a pregnancy because of health problems or reproductive system issues.
Remedy for female infertility
- Operation
- Ovulation induction (using hormone treatment)
- Assisted reproductive technology (ART)