5 Physical Therapies to Get Treated for Knee Osteoarthritis
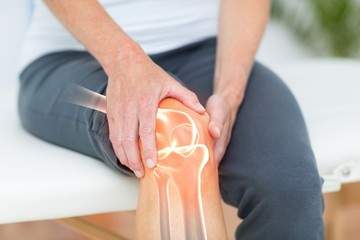
Knee Osteoarthritis is a condition that causes pain in the knee, limiting the person’s ability to walk easily, exercise, or climb stairs. It is one of the most common causes of knee pain. The condition occurs due to the wearing away of the cartilage that acts as a cushion for the bones in the knee joint. Physical therapy effectively treats the pain in the knee caused by osteoarthritis and increases the range of motion.
What Is Knee Osteoarthritis?
Cartilage is a soft and flexible tissue present between the joints in the bones. It acts as a cushion for the bones and stops two bones from rubbing against each other, thus preventing damage.
As people get older, their body weight leads to the wearing away of the cartilage, thus resulting in the rubbing of two bones. It causes swelling, stiffness, and pain. This condition is termed osteoarthritis.
Knee osteoarthritis is the wear and tear of the cartilage in the knee joint. The condition affects the bone underneath the cartilage and also the nearby soft tissues. It causes the synovial fluid within the knee to become less sticky and results in the rubbing of knee bones.
It is common in overweight women and also occurs as a result of a traumatic knee injury. Athletes who play soccer, tennis, and those involved in long-distance running put continual pressure on their joints, thus increasing the risk of developing knee osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis
The following are the signs and symptoms of knee osteoarthritis.
- Pain in knee, caused while bending or straightening it
- Severe pain while carrying weights
- Swelling as a result of excess fluid buildup in the joint
- Bone spurs or osteophytes that occurs when the cartilage breaks down
- A feeling of warmth in the joint, especially at the end of the day
- Popping or cracking feel while bending the knee
- Stiffness when moving the knee joint, especially in the morning
- Decrease in the mobility of the knee
Physical Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis
During the first visit to a physical therapy clinic, the physical therapist asks for medical history and examines the patient’s symptoms, activity level, and pain intensity. The therapist will perform a physical exam to measure the range of motion, strength, flexibility, and mobility of the knees. These analyses help them to provide the patient with individualized treatment.
1) Stretching and Range of Motion Exercises
When the knee joint movement is abnormal, it can worsen the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Physical therapists assess the range of motion of the affected knee by comparing it with the regular movements of the healthy knee to come up with stretching and range of motion exercises.
These exercises help the patient to bend and straighten the knee and improve flexibility. Some exercises include hamstring stretch, calf stretch, heel raises, straight leg raise, and side leg raise.
2) Strengthening Exercises
The wear and tear of the cartilage make it challenging to maintain strength in the muscles near the joint. In addition to that, people with knee osteoarthritis also experience hip muscle weakness. Hence it is essential to strengthening those muscles to experience an increased instability throughout the body.
These exercises reduce pain, increase function and range of motion, and maintain healthy cartilage. Seated leg raises, side-lying leg raises, and squats are some of the strengthening exercises that make the muscles stronger. Aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, pilates, and yoga could also do great benefits.
3) Manual Therapy
Physical therapists use their hands to gently move the muscles and joints in the knee to improve strength, motion, flexibility, and induce relaxation in patients. Some of the manual therapy techniques include soft tissue mobilization, trigger point therapy, and acupressure. When manual therapy is used in combination with electrotherapy and therapeutic exercises, it helps to reduce pain in the knee and increase function.
4) Heat/Cold Therapy
Heat therapy increases the flow of blood and brings enough oxygen and nutrients to the knee area. Physical therapists suggest using heating pads to apply over the knee gently. It reduces muscle spasms, relieves tension, and reduces pain.
Cold therapy slows down the blood flow and reduces inflammation in the knee. Physical therapists suggest using ice cubes wrapped in a towel to carry out cold therapy. It helps in knee pain relief and reduces swelling.
5) Therapeutic Ultrasound
Therapeutic ultrasound works on a deep heating mechanism that uses sound waves to treat the deep tissues. When the physical therapist applies sound waves safely against the skin, it creates a vibration in the deep tissues, thus increasing heat and friction in the knee joints. This process starts the recovery process and reduces pain and inflammation.
Final Thoughts
Knee osteoarthritis is a painful condition, but one needs to stay active in order to improve knee joint mobility and achieve pain relief in the knee. Involving in physical activities is an effective way to treat knee osteoarthritis. Maintaining an active lifestyle also helps overweight individuals to lose weight which is one of the primary causes of osteoarthritis.